Single covalent bond
Formation of a covalent bond by sharing of one pair of electrons i.e. two electrons are involved is called a ‘single covalent bond’, or simply a single bond. A single covalent bond is represented by a small single line ( ) between the two atoms.
Formation of single covalent bond is illustrated through the following example.
Formation of Hydrogen Molecule:
Hydrogen atom has only one electron in its outermost shell. Hence it requires one more electron to acquire the nearest noble gas configuration of helium (He: 1s2) i.e. only one electron occupies the 1s-orbital of the hydrogen atom.
For this each hydrogen atoms contribute one electron to other to share one pair of electrons between them. This leads to the formation of a single covalent bond between the two hydrogen atoms. The electrons in the hydrogen atom are spinning in opposite direction and hence overlapping of atom take place. There will be decrease in potential energy due to sharing of electrons between the atoms.
Formation of s-orbital take place in this bond. This leads to the formation of a single covalent bond between the two hydrogen atoms as represented in
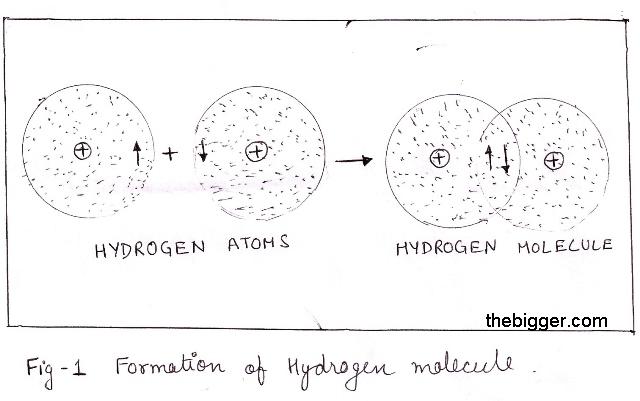
Since formation of Hydrogen atom involves overlapping of s-orbital, the bond formed between the two hydrogen atoms is known as s-s bond. The overlapping of orbital’s takes place along the same axis.
The covalent bond will be stronger when the overlapping between the atoms is larger.
Sigma bond: A bond which is formed by overlapping of the orbital along the same axis is called as sigma bond.
H• + •H ——-> H: H ——-> H―H
